
original in en Georges Tarbouriech
Georges is a long time Unix user. He likes products that contributed to the spread of free software solutions in the professional area.
MySQL and Perl have been around for quite a while. They are still
widely used even if the "fashion" is changing. This article talks about
these two products working together as a whole, either on the Internet or on
your local network. The provided example is written for Unix systems, free or not,
even if it can be adapted to other widespread "systems".
What this article is : a small review of what can be done with this pair,
showing ease of use, speed, reliability, security...
What this article is not : neither a MySQL tutorial nor a Perl tutorial;
neither a MySQL review nor a Perl review.
Accordingly, we'll see MySQL at work in combination with Perl, without
forgetting that "there is more than one way to do it".

MySQL is a Relational DataBase Management System (RDBMS) available from
http://www.mysql.com. It's released under GNU GPL
for free depending on what it is used for. Check the licensing policy on the
MySQL's website. It works either as a server or a client on many platforms.
A few other RDBMS exist as free software and we won't make any comparisons
since the choice of MySQL for this article is arbitrary. Neither will we
compare to the big "commercial" guns such as Informix, Oracle, Sybase...
It is enough to say that MySQL is probably one of the most widely used DBM on the
Internet. For this article we'll use the version 3.23.36 (again,
arbitrarily). At the time of this writing, the current stable version is
3.23.46 and the experimental one is the long awaited version 4.0. These can
be downloaded as source code to be compiled or as packages.
To use MySQL in conjunction with Perl, you need some more stuff : the Perl
DBI modules. At least, you can download DBI, Msql-Mysql-modules, Data-Dumper
and Data-ShowTable.
We won't talk about their installation since it's obvious and the packages
provide you with everything you need to know.
Perl stands for Practical Extraction and Report Language. At the
beginning, it was intended for document manipulation (parsing, extracting...) but
it quickly became much more than this. You can do almost everything with
Perl. From administration tasks to cgi scripts via true applications and of
course, database interfaces.
Perl is part of many (if not all) Unix distributions whether they are free or
not. The current stable version is 5.6.1 and the experimental is 5.7.2 at
the time of this writing. For the article we'll use the good old one,
5.005_03. In case you don't have Perl installed on your machine (how can
this be possible ?) you can get it from http://www.perl.com. Perl
provides you with tons of modules for almost everything. You can get them from
the CPAN section of this website : a goldmine !
Last but not least, to work with both tools, surprise : you need a webserver
! Apache seems the right choice since it's part of many Unix distributions,
free or not, as usual. In case you don't have it (where did you find your
distro ?), it's available from http://www.apache.org.
You probably noticed that LinuxFocus is a multilingual magazine. That means,
when you're an editor, you need to manage the status of new articles, their
translation. In other words, who is doing what, when... At the moment, there
are about 200 articles available, on average in 5 languages. That makes
about 1000 articles (how clever am I ?) and still counting ! This stuff
has to be archived, formatted, summarized... How do you think this management
is done ? With Perl, of course.
Our editor in chief, Guido Socher, wrote a lot of
Perl programs to make our work much easier. He wrote as well a three parts
Perl tutorial and a Perl book review. Check the reference section at the end
of the article.
Javi, the Spanish editor, wrote a program to manage the translation status... in
Perl.
Atif, one of our star authors, comes from Perl kingdom, that's why his
mother tongue is Perl. Eventually, he also contributed to MySQL, improving
a web administration tool. Again, check the references section.
All this to say that if you look for a Perl paradise... join LinuxFocus.
Since I'm one of the French LinuxFocus editors... and I'm rather lazy, I created my own
LinuxFocus database using, guess what : MySQL and Perl !
This assumes MySQL has been properly installed, users have been created and
have been protected with passwords. Installation is not in the scope of this
article and the great documentation provided with MySQL will tell you
everything.
Start the MySQL server using the mysql.server script, since it invokes
the safe_mysqld daemon and you can pass options to this daemon.
Connect to the server using
mysql -h host -u user -p
If the server is running on your local machine then you don't need -h host.CREATE DATABASE lf;
This is our example (lf stands for LinuxFocus) and obviously you give the name you want to your own database. Next, grant some permissions to the allowed users, this assumes you have the right to do it (that is you have administration right as the connected user). If you want a user to be able to manage the database you can give him the privileges to do so usingGRANT ALL ON lf.* TO username;
Select the database you just created by typingUSE lf
Create a table according to your needs. In our example, we create a table called trissue :CREATE TABLE trissue (num INTEGER UNSIGNED, category VARCHAR(25), title VARCHAR(40), author VARCHAR(20), en VARCHAR(20), es VARCHAR(20), fr VARCHAR(20),de VARCHAR(20), nl VARCHAR(20), ru VARCHAR(20), tk VARCHAR(20), issue VARCHAR(20));
Let's check, it has been created as expected with :
USE lf
SHOW TABLES;
DESCRIBE trissue;
LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE "maindb.txt" INTO TABLE trissue;
If your text file is correct the table is now populated. You can check it with :SELECT * FROM trissue;
This should display a long list. Now, you're able to retrieve any type of data using queries.
Perl will help us to automate the queries, to display the results in a web
browser, etc. Again, this implies the Perl modules have been properly
installed to use MySQL in combination with Perl.
We now will write Perl scripts to be used as cgi scripts. They will allow us
to mix Perl and HTML to query the database and format the output.
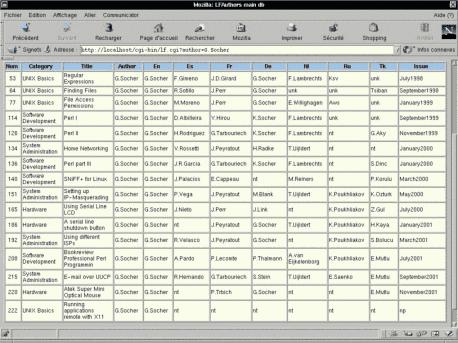
We'll use a simple example script, allowing us to search all the articles
written by the same author. We will display the article numbers, the
category, the title, the translator's names for
the different languages (only the full working projects), the issue when the
articles have been published.
You can use this script as a model for your own use, but be aware
that this example is not a very secure program. You can download a more
commented version from =>here<=.
#!/usr/bin/perl -Tw
# First, we say this is a "Tainted" Perl script.
#
# This is a comment
# db consult
#
# We use the Perl DBI module
use DBI;
# As cgi :
use CGI qw(param());
print <<END_of_start;
Content-type: text/html
<html>
<title>LFAuthors main db</title>
<center><TABLE>
<TR VALIGN=TOP>
<TD><form action="/cgi-bin/lf.cgi" method="get">
# Here comes the button's title for the launching page
<input type="submit" value=" LFAuth ">
</form>
</TD>
</TR>
</TABLE>
<center><H2>Search by author</H2></center>
<form action=\"/cgi-bin/lf.cgi\" method=\"get\">Author name : <input
type=\"text\" size=\"30\" name=\"author\"><input type=\"submit\"
value=\"Search...\"></form></center>
END_of_start
if (param("author") ne '') {
$author = param("author");
$autsrch.='"';
$autsrch.=$author;
$autsrch.='"';
# We connect to the database named lf as user doe
$dbh = DBI->connect("DBI:mysql:lf","doe",'');
$sth = $dbh->prepare("
select *
from trissue
where
author = $autsrch
");
$sth->execute;
print <<END_suite;
<center>
<TABLE BORDER=>
<tr bgcolor=#A1C4EE>
<th width=60 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Num </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Category </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Title </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Author </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> En </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Es </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Fr </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> De </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Nl </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Ru </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Tk </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Issue </font></th>
</tr>
END_suite
while( ($num,$category,$title,$author,$en,$es,$fr,$de,$nl,$ru,$tk,$issue) =$sth->fetchrow() ) {
print "<tr>";
print "<td width=60 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=center> $num</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $category</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $title</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $author</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $en</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $es</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $fr</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $de</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $nl</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $ru</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $tk</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $issue</td>";
print "</tr>";
}
print "</TABLE>";
print "<BR>";
print "<BR>";
print "<br>";
} else {
# DB Connect
$dbh = DBI->connect("DBI:mysql:lf","doe",'');
# Search
$sth = $dbh->prepare("
select *
from trissue
");
$sth->execute;
# Display result
print <<SUITE;
<center>
<TABLE BORDER=>
<tr bgcolor=#A1C4EE>
<th width=60 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Num </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Category </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Title </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Author </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> En </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Es </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Fr </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> De </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Nl </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Ru </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Tk </font></th>
<th width=110 align=CENTER><font color=#000000> Issue </font></th>
</tr>
SUITE
while( ($num,$category,$title,$author,$en,$es,$fr,$de,$nl,$ru,$tk,$issue) =$sth->fetchrow() ) {
print "<tr>";
print "<td width=60 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=center> $num</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $category</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $title</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $author</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $en</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $es</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $fr</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $de</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $nl</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $ru</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $tk</td>";
print "<td width=110 bgcolor=#FFFFE8 align=left> $issue</td>";
print "</tr>";
}
print "</TABLE>";
print "<BR>";
}
print end_html;
$sth->finish;
# Disconnect
$dbh->disconnect;
exit;

Obviously, if you wish to provide a database service on your website you must
secure the whole thing. Of course, we won't give a step by step way to secure a
website or a database server. However, it's important to insist on the basics.
To make it short, when you provide services on the web, the first thing you must
secure is your web server. This is far beyond the scope of this article. If you
want to learn more on the subject, there is plenty of documentation available.
A nice place to start is the Linux Documentation Project.
The next step concerns the database server. When installing a tool such as
MySQL don't forget to read the security part of the manual. Again, the
basics concern user passwords : don't ever leave an account without
password especially the root account for the database (which should be
different from the machine root account). The other important point is about
permissions : don't grant everything to everybody. It seems obvious... and
that's why many people forget about it !
Going a bit further, why not chrooting the database ? Check Mark's article "Chrooting all services"
in this issue . He talks about a different database but what he
says can be applied to MySQL.
Another security measure concerns the data circulation. It is not a bad idea to
send and receive the data through a tunnel. You can check the Through the tunnel article for more
information.
Last but not least, secure programming is one of the keys. Perl is a great
language, but it's quite easy to make programming mistakes with it. Another
LinuxFocus article will teach you what to do, especially with Perl. Have a
look there. It's the last article of the
Secure Programming series and it especially concerns cgi scripts. A "must
read" !
Of course, this assumes you already have a hardened system without well
known security holes, with latest patches, and many required security tools
such as NIDS (Network Intrusion Detection System) like snort (from http://www.snort.org), firewall, port and
security scanners (nmap, nessus), etc.
If you can afford it, you can also have a different server for each provided
service : one web server, one database server... and the mirrors for high
availability. And so on ! You never end with it, since security is never
achieved. You just try to reduce the risks... and they're getting worse
every day. You've been warned.
As There Is More Than One Way to Do It, you can choose your own way. There are
many RDBMS and many languages to communicate with them. The idea behind writing
this article was to show how MySQL and Perl work fine when used together.
Of course, the choice was quite subjective : I love MySQL because it's rather
small in size, it works on many OSes, it's fast, reliable... I also much appreciate the
work done by the MySQL team, without forgetting the numerous contributors. And
what I like most: those people didn't try to reinvent the wheel. They kept
things simple.
Concerning Perl, everything has been said about it : what could I add ? I
believe you can't work without it, either if you are a network administrator or
a developer, or whatever. The Perl community is one of the greatest sources for
knowledge sharing out there. A magazine is available, called the Perl Journal,
which is now included in SysAdmin magazine, every two issues. If you want to
subscribe, go to http://www.samag.com.
Since we are talking about great work, here comes the usual off-topic section.
Our LinuxFocus readers haven't probably noticed the small number of persons
involved in the magazine. Nevertheless, you can read it in many different
languages. Did you ever noticed that some of the teams work with almost always,
only one or two persons doing the whole job ? They are webmasters, translators,
etc. Check the Russian team, the Turkish team : you'll find most of the articles
are translated by Kirill or Erdal. Check the projects under development, such as
Portuguese or Arabic : same result ! I'd like to congratulate all of them for
the great job they do. Thanks to all of you : the free software community owes
you a lot.
Sorry for the digression, but I believe this had to be said.
Back to the subject, let's finish with a few words about free software. People
at MySQL or Perl deserve many thanks. They provide you with great tools mostly
for free. However these tools are often as good as true commercial products (if not
better), they are frequently updated, very well documented and you can use them on almost every Unix
systems. Can you find the equivalent somewhere else ? I'm afraid not !
This article will probably not teach you much, however if it makes you feel like
trying those products, it won't be useless.
Aren't we living in a great time ?
Perl.org
cpan.org, the perl archive
Guido's Perl tutorial :
Perl I
Perl II
Perl III
Professional Perl Programming book review :
Perl Programming
Atif's
contribution to MySQL.
A LinuxFocus MySQL review : old article still, up-to-date :
MySQL
An old LinuxFocus SQL two parts tutorial :
SQL Part I
SQL Part II